Abstract¶
This document organizes and reports the analyzes on the data collected in an opinion survey carried out to determine the perception of Brazilian consumers about the consumption of organic foods. It also issues considerations and suggests measures when results thus make them relevant.
Executive Summary¶
Problem Statement¶
There is a perception that the organic food market is accelerating. This feeling is feed by some facts among others:
- The support for organic production is present in several government actions, which offer special lines of financing for the sector and encourage projects for the transition from traditional crops to organic production.
- There is a global trend on green business, that is, sustainable enterprises that have production and distribution activities based on social-environmental development that promotes improvements in communities and the sustainability of present and future generations.
However, in order to consolidate the idea with concrete data and facts, issues such as these listed below (among others) must be properly addressed:
- Consumers are increasingly interested in sustainability and healthier food. And they are willing to pay more for these differentials.
- It is subjective knowledge that national organic production has been growing by more than 20% a year. However, this growth is lower than the demand for products.
- The imbalance between production capacity and demand for the product on the shelves has given headaches to retailers across Brazil and this could drive the market.
This work aims to contribute to the solution of the above demands.
Analysis and Results Equating¶
In order to bring the answers to the above, the present study establishes the following goals that will support the necessary inference in conducting the solution of the problem:
- Perform quantitative research for evaluation of the consumption of organic products in Brazil
- Identify the profile of the consumer of organic products
- Evaluate the products and more concepts associated with organic
- Evaluate the criteria of choice of organic products such as: brands, stores, packing, between others
- Determine the mood for the consumption of organic products in one near future
Conclusions and Recommendations¶
We learned that the market for organic products in Brazil is a modest 31%. But this tag has been showing a growth of 63% compared to 2019 and 106% compared to 2017 data.
The derivative of this movement indicates a promising market, as it is 240% in the 2019/2021 period than in the 2017/2019 period.
If the prerogatives of the other 69% (not buying due high price) are properly fought (easy due the obvious target), there is room for further growth.
There are 71% of consumers who buy organic products even though they think the price is too expensive (44%) and declare it to be justified, this combined with the feeling of belonging to a class (such as the growth in the use of the seal of origin) can indicate strong loyalty and help from these consumers in the form of direct advertising in reducing the share of 69% rejection group.
According to data from Sebrae in Brazil, the size of the global organic market should reach the level of U 199 .2 billion. In Brazil, the forecast for 2021 was USD 0.95 billion, reaching USD 1.77 billion in 2026, an increase of 86.3%. 200 to 1 represents a good possibility of growth in a market with good absolute numbers.
The present study only looked at the interface with consumers (buyer side) . Some future developments can come to mind in order to complement this knowledge base:
Correlation of the behavior of these consumers with others who live in countries with possibly different cultures and habits.
Observation of behavior on the other side of the counter (seller side), determining the number of players and their tendency to invest in the area.
Data Analysis¶
This section demonstrates the data and concepts used to work the goal of achieving the previously stated objectives.
Background¶
The work sequence of this study obeys a methodology that favors the capture of simple although meaningful data. It shall be used to consolidate a solution to frequent issues in the process of financial decisions or market investment. Correlations, clustering and regression estimates were not used. Efforts are focused at:
- Attention was given to dispersion of data capture and sampling methodology.
- Consumption habits were determined.
- The triggering factors of the purchase event were determined.
- Possible barriers to consolidation of the purchase event were determined.
- The perception of price inequality between organic and non-organic products was equated in order to identify the opinion of consumers.
Sampling Methodology¶
- Technique : Research carried out through personal and individual interviews, using a questionnaire structured and with average duration of 12 minutes. The approach took place at points where population usually flow. The questionnaire was designed according to the objectives established by _____ . The data collection period took place between September 15th and October 5, 2021.
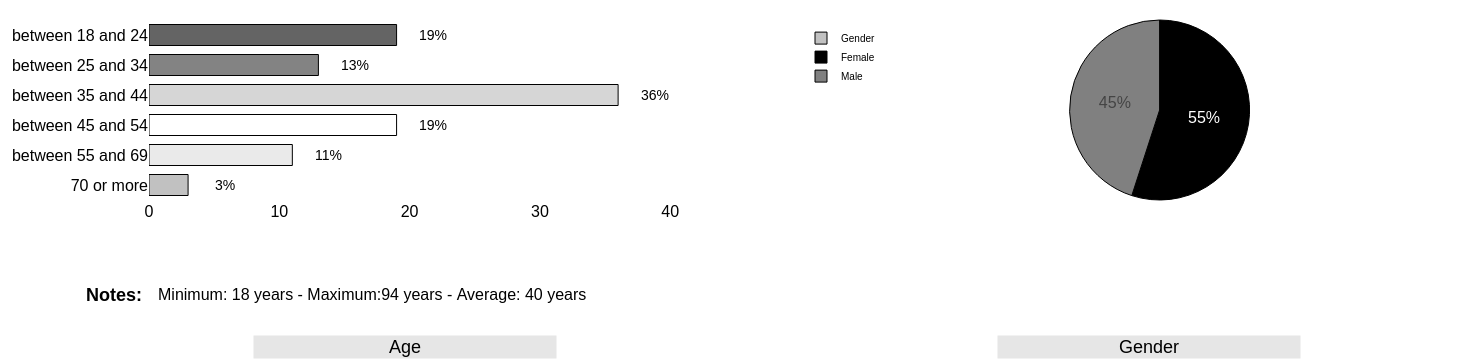
- Universe : Brazilian population, responsible for the purchase of consumables of the residence, aged 18 or more, residing in the municipalities selected to compose the sample.
- Sampling : The 987 respondents were probabilistic selected in three steps.
- In the first the municipalities were drawn.
- In the second step, the amount of interviews to be held in each municipality was established to from the PPS method (Proportion Proportional to Size) leading into account the size of the county.
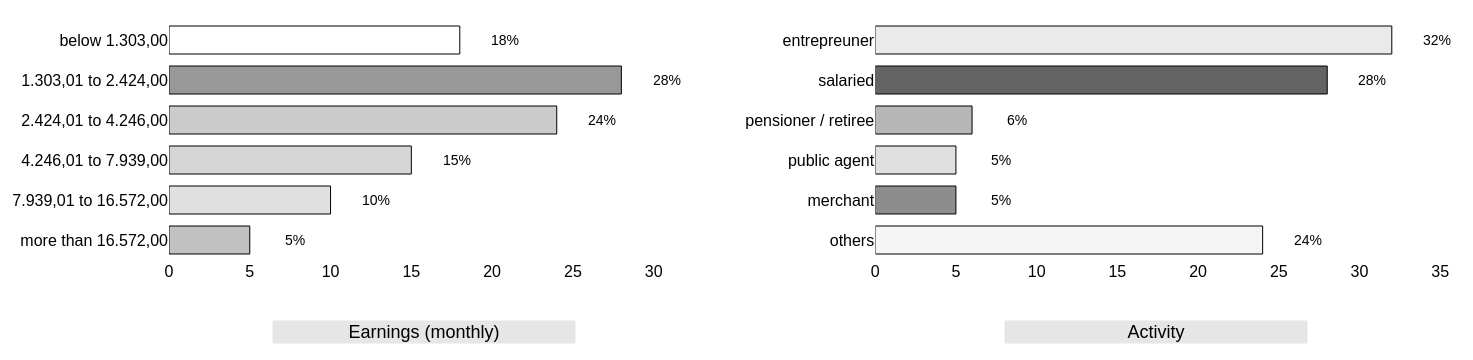
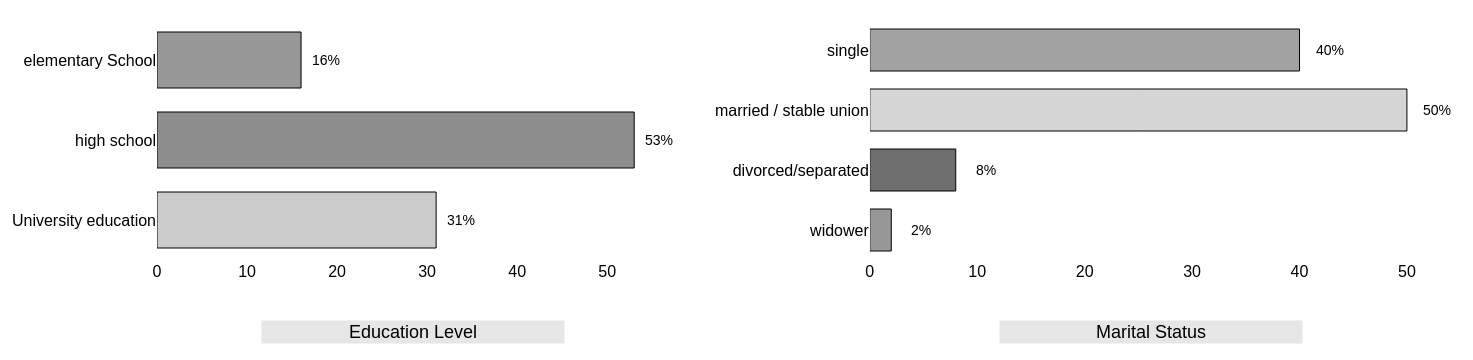
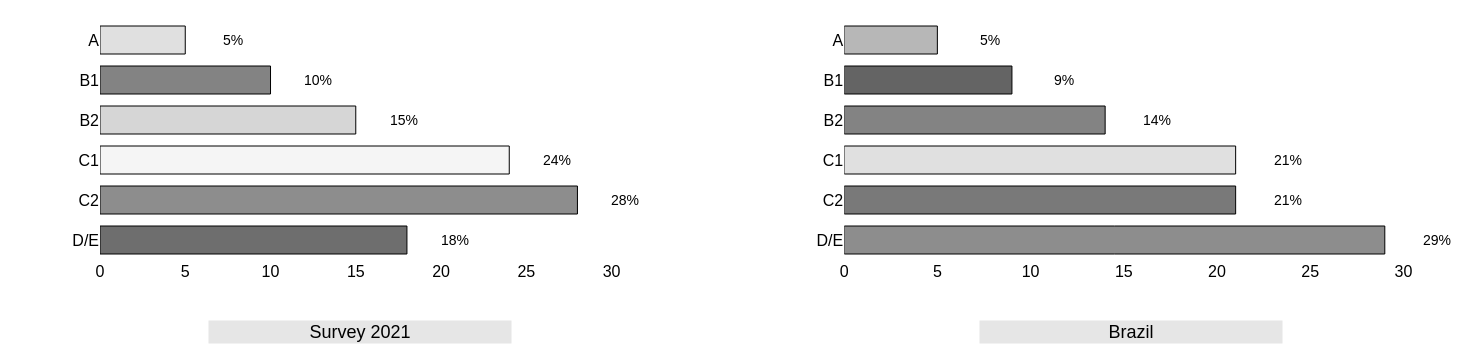
- In the third and final step, the sampling units were selected from the each stratification criteria as e.g. sex, age group, education and, social class. This sampling objective was to calculate consumer penetration of organic products.
- Level of confidence and margin of error : The selected sample is statistically significant of the universe under study and reaches a 95% confidence level for an estimated margin of error, considering a simple random sample of approximately 3.1 points percentages for more or for least about the general results.
Results and Analysis¶
The following blocks address in sequence each aspect of the road map depicted on the background section above. Opinionated takeaway notes are provided in non exhaustive manner.
Sample Preparation : this section qualifies the samples observing the unique properties (e.g. as social presence), spatial dimension (e.g. as geographic dispersion) and time dimension (e. g. when an event is occurring).
¶
Geographic and Time Dispersion : How samples are dispersed on the space and time and how the methodology reach them.¶
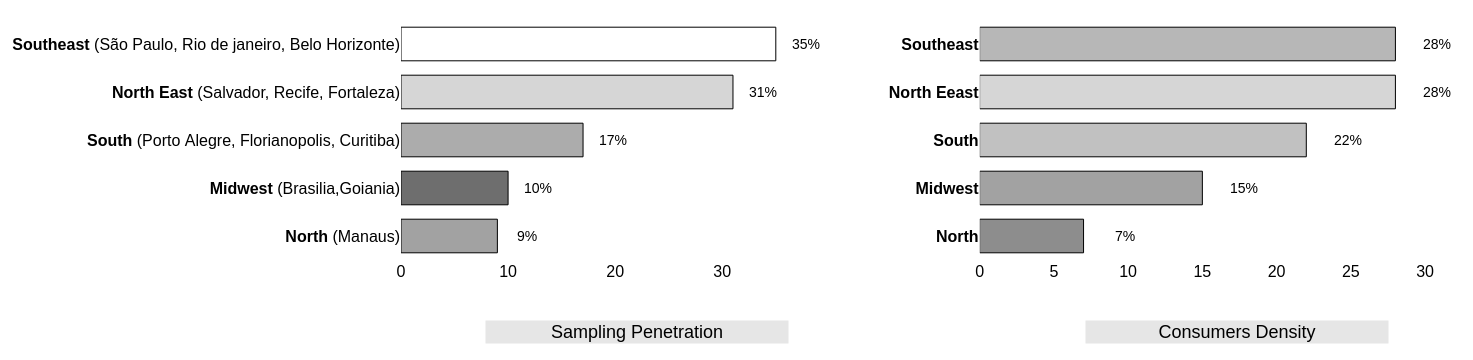
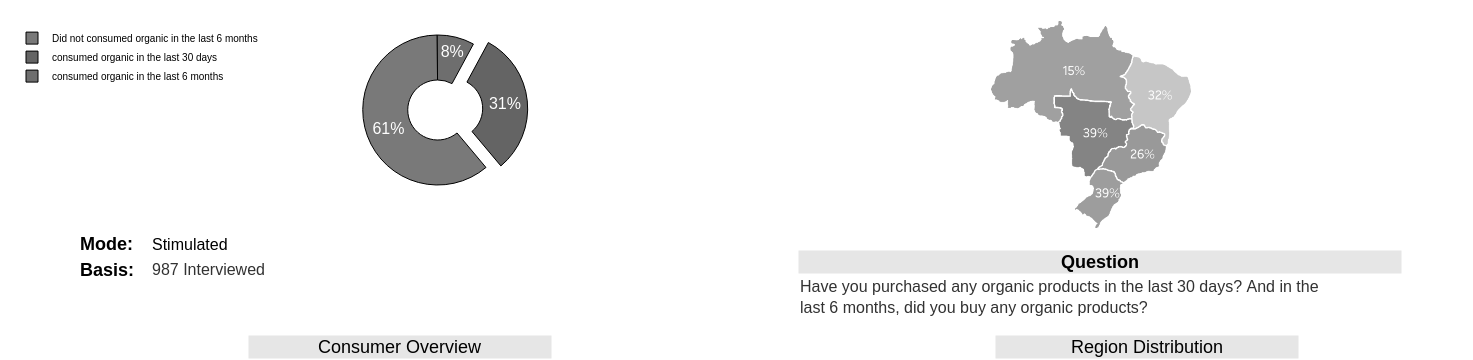
- We saw above that from a sample size of 987 items, 31% used organic products during the last month.
- The research will focus mainly on them from now on.
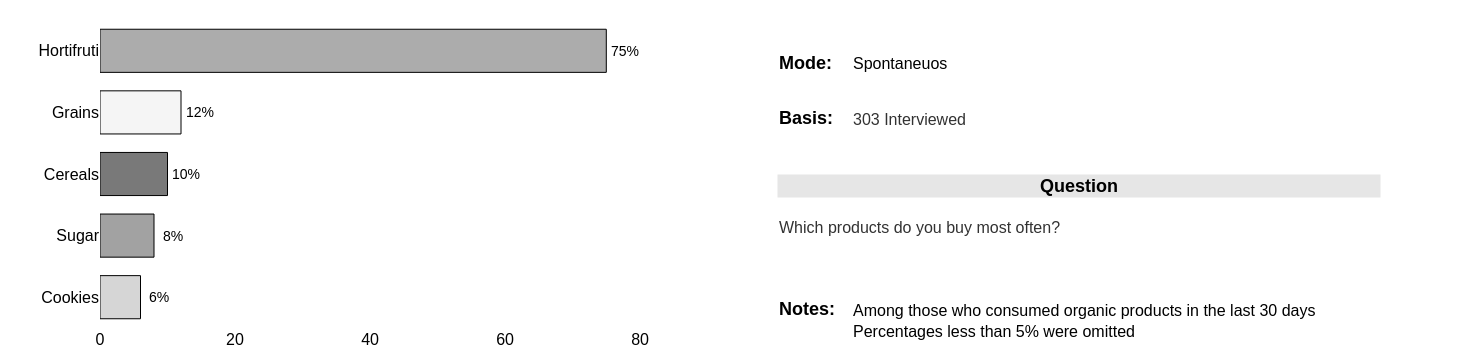
Most consumed organic products
The purchase of organic products is still strongly related to fruit and vegetables (75%).
This preference can be seen as a gateway to expanding consumption of the other products.
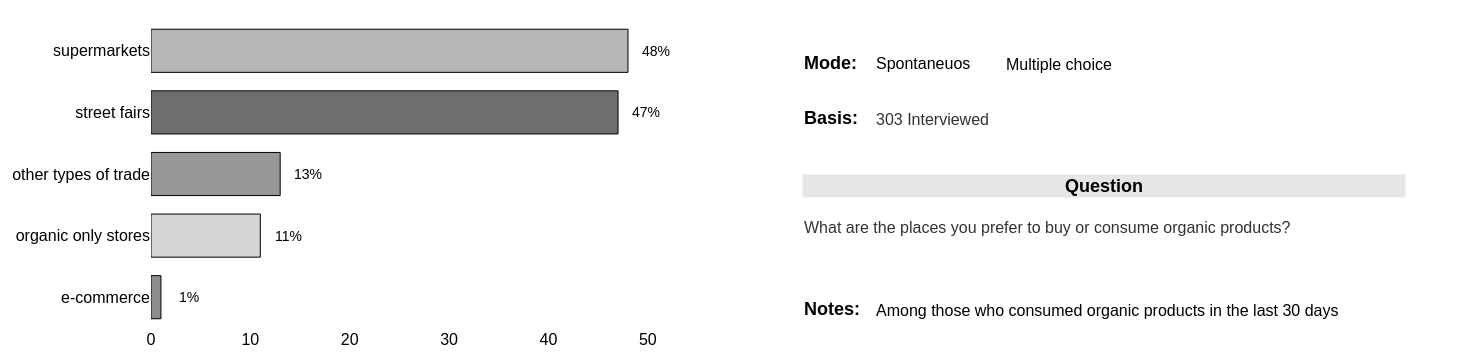
Favorite places to buy organic products
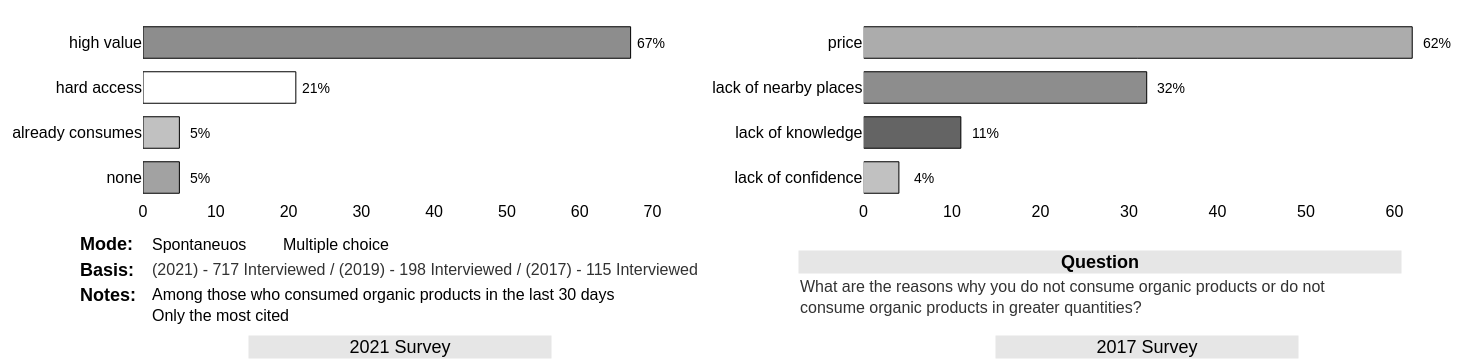
Supermarkets (48%) and street fairs (47%) are the most cited places for buying organic products, a drop of 21% and 45%, respectively, compared to 2019.
A significant portion migrated to stores that sell only organic products.
It was 4% in 2019 and jumped to 11% in 2021, a jump of 175%.
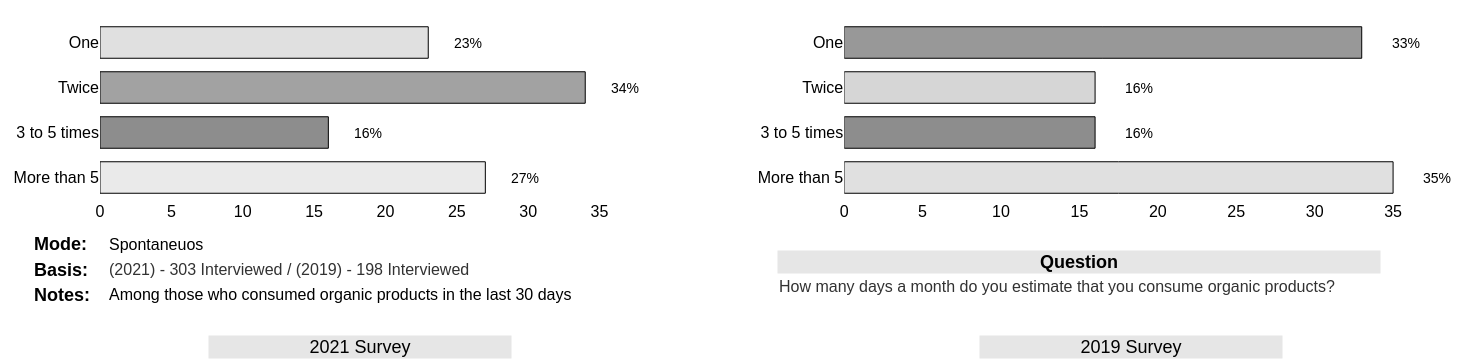
Frequency with which you consume organic products
34% of organic consumers declare, in 2021, that they buy on average 2 times per week. An increase of 112% from that 16% in 2019.
¶
Triggers : The mechanisms that operate on consumer decisions inclined to buy or to identify a organic product¶
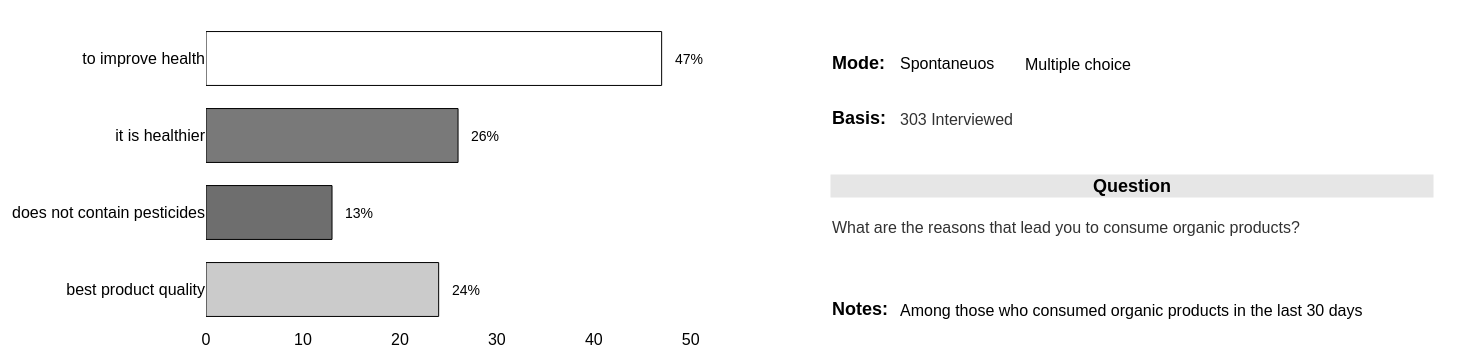
Reasons to eat organic
People claim to consume organic products for individual reasons, the dimension of the collective does not appear in a significant way.
The numbers show the need to insist on publicizing the advantages of organic products in issues that concern society, such as the preservation of the environment, the climate crisis and the reduction of socioeconomic imbalances, among others.
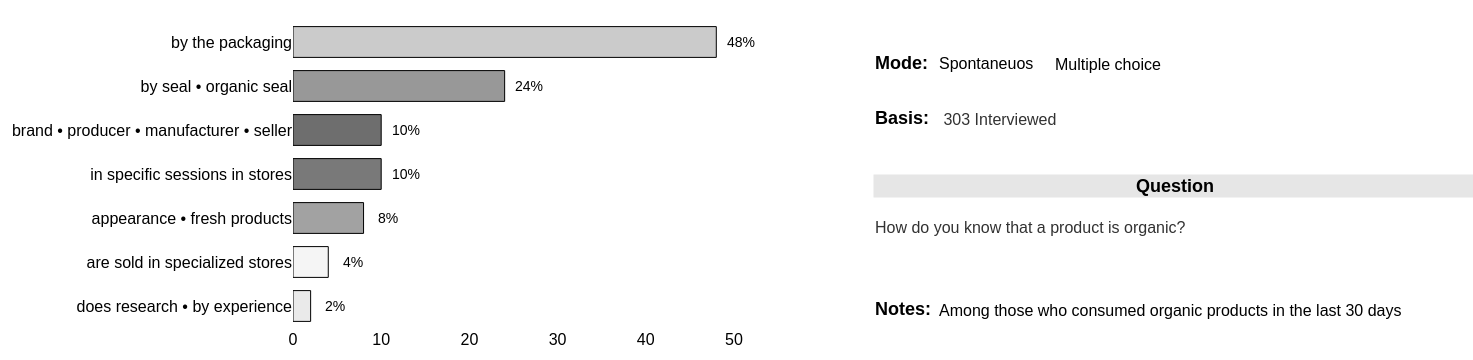
How do you know that the product is organic?
Product recognition by the organic seal jumped from 3% in 2019 to 24% in 2021, an increase of 700%, demonstrating the growing importance of certification and its correct display on packaging and points of sale.
Product appearance followed the opposite path, dropping from 12% in 2019 to 8% in 2021.
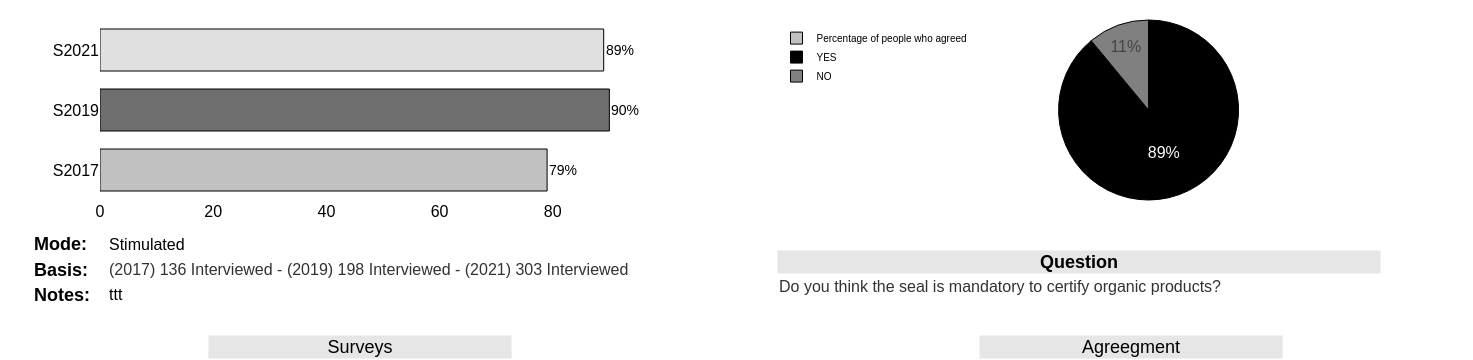
Perception regarding the obligation of the seal 89% say they know that the seal is mandatory to certify that a product is really organic.
In the Midwest, this percentage rises to 97%.
¶
Barriers : Mechanisms that prevent a consumer to buy an organic product or increment the frequency of acquisition.¶
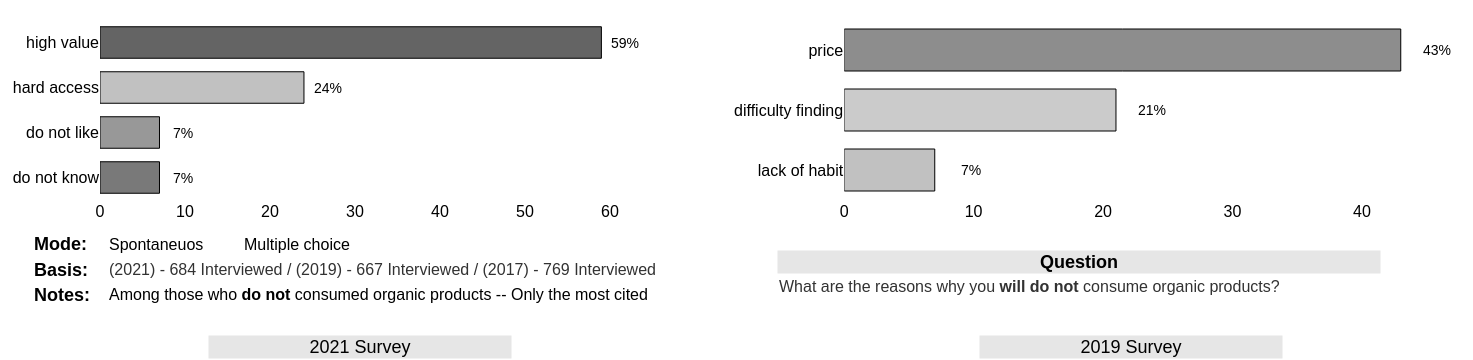
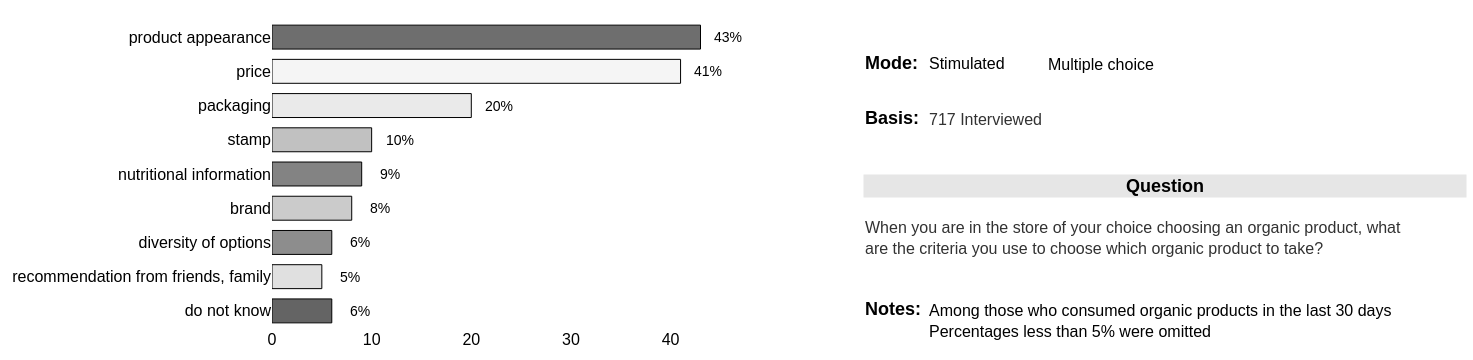
Price perception is dominant
Consumers (69% of them) do not buy organic products due to the high price - period.
This indicator has increased since the last survey (from 43% to 59%)
Even the 31% who buy show inertia in the increase in consumption due mostly to the same indicator (price)
There is a marginal perception (20%) that there is difficulty in accessing products.
¶
Price Perception : Aspects that influence the concept of worthiness of the organic products compared with cheaper regular ones.¶
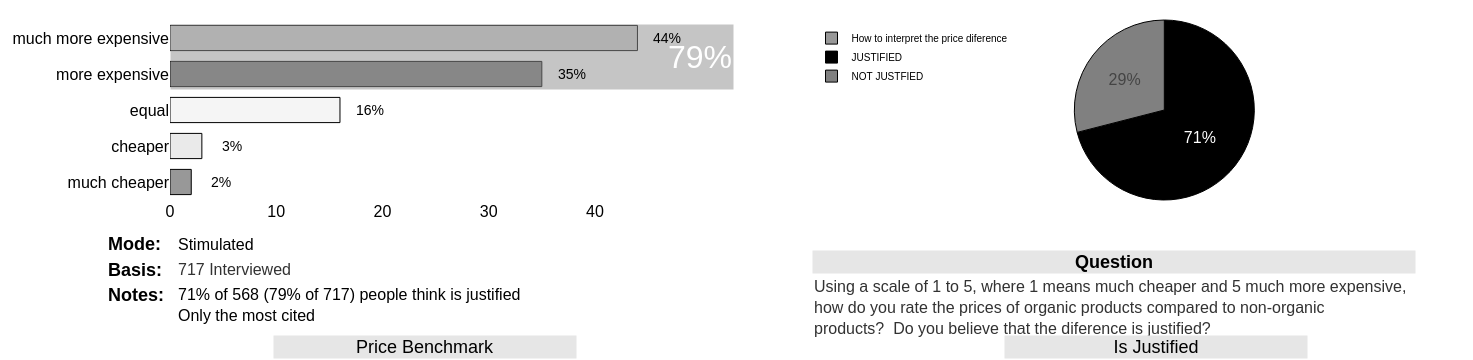
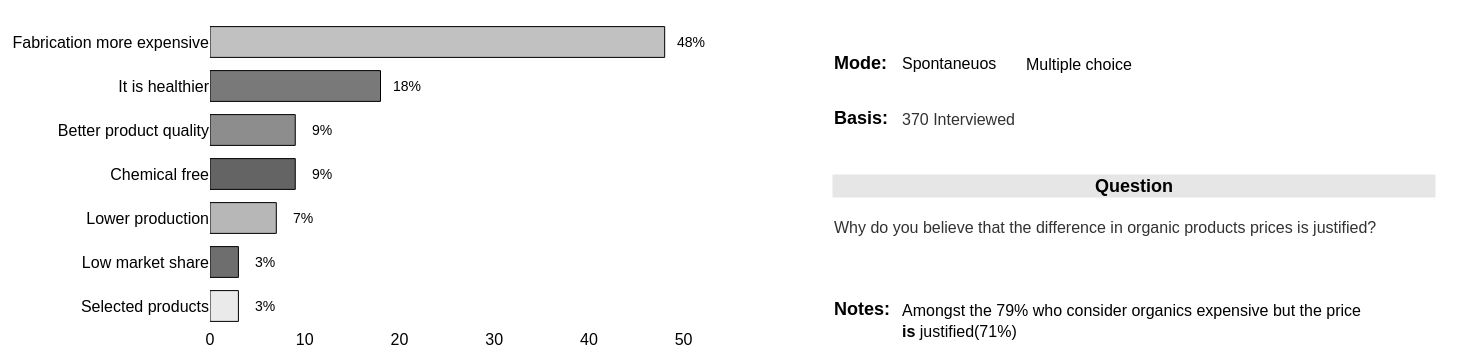
- There is a solid perception (79%) that organic food is more expensive than its competitors. A strong indicator is the 'much more expensive' tag at the 44% indicating significant inertia in a possible change of heart move.
- However, 71% understand that the fact is justified and the majority (48% + 16%) attribute to factors which, in most cases, the observer does not have mastery of the technique to correctly assess (productive processes and health science).
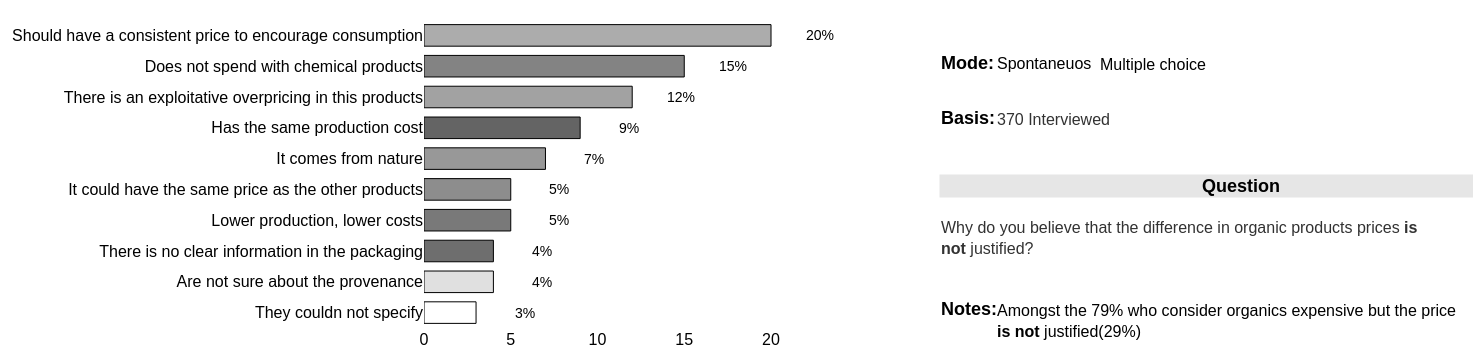
- The 29% who understand the difference to be unjustifiable have a more diffuse perception of the reasons (the main factor scoring only 20%). The perception that the production process and market policies do not match the product are decisive in the four main reasons (totaling 56%)
Conclusion¶
Please see notes on the Executive Summary.
Recommendations¶
Please see notes on the Executive Summary.
4. References & Notes :¶
**This research is at public domain because it was based on (public) data from **https://organis.org.br/
Created by : msantrax@gmail.com